- Published on
Understanding JavaScript's Prototype Pattern
Understanding JavaScript's Prototype Pattern
JavaScript's prototype-based inheritance is a fundamental concept that sets it apart from classical object-oriented languages. The Prototype Pattern is a key mechanism in JavaScript that allows for efficient object creation and method sharing. This article will explore the Prototype Pattern in depth, using both code examples and a visual representation to clarify the relationships between constructors, prototypes, and instances.
The Prototype Pattern Explained
In JavaScript, each function is created with a prototype property. This property is an object that contains properties and methods that should be available to instances of a particular reference type. The prototype serves as a blueprint for objects created using the constructor function.
Let's examine a basic implementation of the Prototype Pattern:
function Person() {}
Person.prototype.name = "Alice";
Person.prototype.age = 29;
Person.prototype.job = "Software Engineer";
Person.prototype.sayName = function() {
console.log(this.name);
};
let person1 = new Person();
person1.sayName(); // "Alice"
let person2 = new Person();
person2.sayName(); // "Alice"
console.log(person1.sayName == person2.sayName); // true
In this example:
- We define an empty
Personconstructor function. - We add properties (
name,age,job) and a method (sayName) toPerson.prototype. - We create two instances of
Person:person1andperson2. - Both instances can access the
sayNamemethod, which outputs thenameproperty. - We confirm that both instances are using the same
sayNamemethod.
Visual Representation
To better understand the relationships between the constructor, prototype, and instances, let's examine the following diagram:
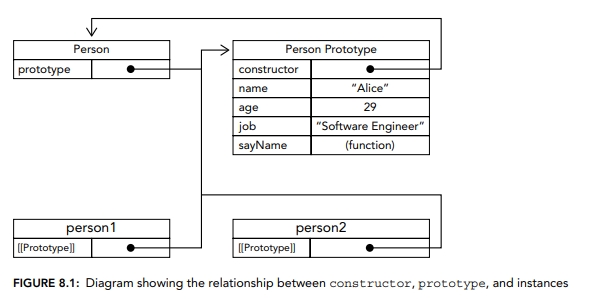
This diagram illustrates several key concepts:
Constructor Function: The
Personfunction serves as the constructor. It's an empty function in this case but could contain initialization logic if needed.Prototype Object:
Person.prototypecontains shared properties and methods. In our example, it includesname,age,job, and thesayNamemethod.Instances:
person1andperson2are instances created using thenew Person()syntax.Prototype Chain:
- The
prototypearrow shows that thePersonfunction has aprototypeproperty pointing toPerson.prototype. - The
[[Prototype]]arrows (also known as__proto__in some browsers) show that bothperson1andperson2have an internal link toPerson.prototype. - The
constructorarrow at the top demonstrates thatPerson.prototypehas aconstructorproperty pointing back to thePersonfunction.
- The
Method Sharing: The diagram shows that both instances share the same
sayNamemethod, which is defined onPerson.prototype.
How Prototypes Work
When you access a property or method on an object in JavaScript, the engine first looks for it on the object itself. If it's not found, it looks up the prototype chain:
- It checks the object's immediate prototype (its
[[Prototype]]or__proto__). - If not found, it continues up the chain to the prototype's prototype.
- This process continues until the property is found or until it reaches the end of the chain (typically
Object.prototype).
This mechanism allows for efficient memory usage, as methods are shared among all instances rather than being duplicated for each object.
Benefits of the Prototype Pattern
- Memory Efficiency: Methods are defined once on the prototype rather than on every instance.
- Dynamic Updates: Adding a method to the prototype makes it immediately available to all instances.
- Flexibility: You can override prototype properties and methods on individual instances if needed.
Conclusion
The Prototype Pattern is a powerful feature of JavaScript that enables efficient object creation and method sharing. By understanding how constructors, prototypes, and instances are related, you can write more efficient and flexible code. The visual representation provided in this article helps to clarify these relationships and the underlying mechanics of JavaScript's prototype-based inheritance system.
As you continue to work with JavaScript, keep in mind the Prototype Pattern and how it can be leveraged to create more efficient and maintainable code structures.